How to Comply with NIS2

The cybersecurity landscape is becoming increasingly complex as organisations face evolving threats targeting sensitive data and critical systems. Enter the NIS2 Directive (Directive (EU) 2022/2555), an ambitious EU regulation designed to bolster the resilience of critical infrastructure and ensure enhanced network and information security across member states.
Navigating NIS2 compliance might seem daunting, but understanding its framework and requirements is vital for organisations operating in today’s digital-first environment. Whether you’re an IT professional, a compliance officer, or a representative of a critical infrastructure organisation, this guide will help you master the essentials of NIS2 compliance, offering actionable steps and tools to ensure your organisation is fully prepared.
What Is the NIS2 Directive and Why Does It Matter?
The Network and Information Security 2 Directive (NIS2) builds upon the original NIS Directive (2016) by addressing gaps and inconsistencies observed in its implementation. It aims to establish a harmonised framework for cybersecurity across the EU and strengthens the obligations of organisations that are essential to national welfare and security.
NIS2 is significant because it holds organisations accountable for addressing cybersecurity threats and, in doing so, protects supply chains, public services, critical resources, economies, and citizens. Non-compliance can result in substantial fines, reputational harm, and operational disruption, making it critical for impacted entities to take this directive seriously.
Understanding the Scope of NIS2 Compliance
Not all organisations are affected by NIS2, but for those that are, compliance is mandatory. The directive applies to two primary categories of organisations, each extending across various industries:
1. Essential Entities (EE):
These include businesses and services crucial to maintaining societal and economic stability. Examples are:
- Energy providers (electricity, gas, oil)
- Healthcare organisations
- Drinking water and waste management providers
- Transportation services
- Financial institutions
2. Wichtige Einrichtungen (IE):
These organisations are not as critical as EEs but remain essential to cybersecurity strategies, such as:
- Manufacturers of critical products
- Providers of digital infrastructure, such as cloud and data centre services
- Research and development organisations in key industries
If you’re in doubt about whether your organisation falls under NIS2, assessing the national application of the directive in your member state is a critical first step, as governments identify which entities qualify under each category.
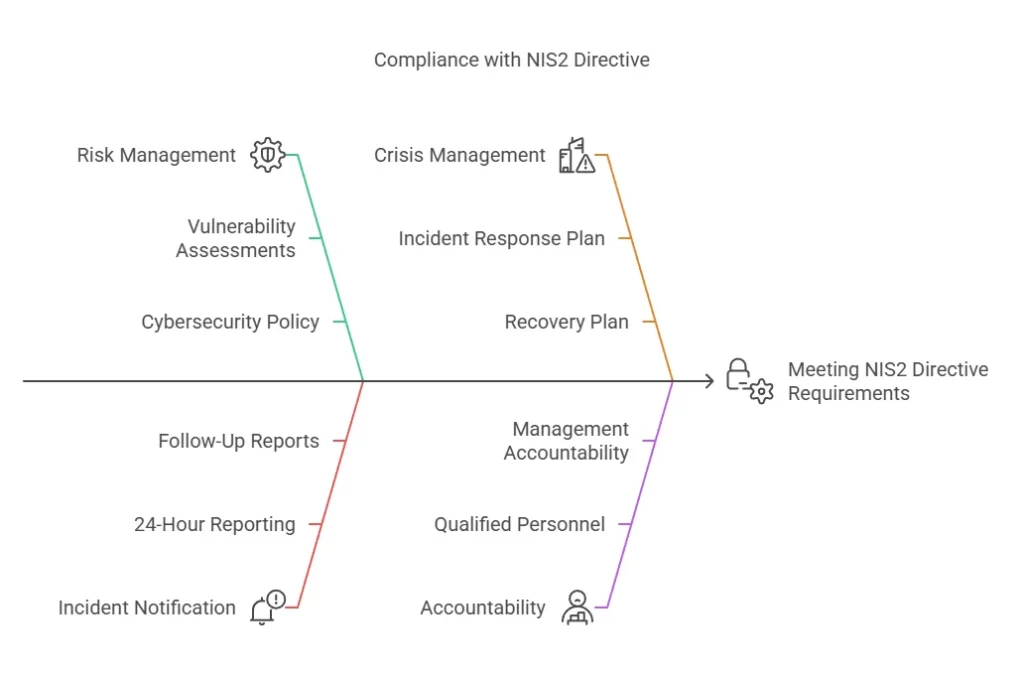
Key Requirements of the NIS2 Directive
1. Risk Management Measures
Implement procedures to identify, evaluate, and address cybersecurity risks, such as:
- Regular vulnerability assessments.
- Establishing a cybersecurity policy covering system updates, encryption, and human error prevention.
2. Incident Notification
Develop processes for reporting any major cybersecurity incidents to the national competent authority (NCA) within 24 hours of detection, with a detailed follow-up report provided within 72 hours.
3. Crisis Management and Business Continuity
Establish a robust incident response and recovery plan, ensuring minimal disruption during cyberattacks and other crises.
4. Accountability and Governance
Appoint qualified personnel such as a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) and ensure top management accepts personal accountability for cybersecurity practices.
5. Cooperation and Information Sharing
Facilitate information exchange with NCAs and cybersecurity bodies, including sharing threat intelligence, vulnerabilities, or attack patterns.
A Step-by-Step Guide to NIS2 Compliance
Here’s how to get your organisation on the right track towards NIS2 compliance:
1. Conduct a Compliance Assessment
- Identify whether your organisation falls under the scope of NIS2.
- Conduct a thorough gap analysis to understand current shortcomings versus NIS2 requirements.
2. Establish Governance Structures
- Appoint leaders accountable for cybersecurity (e.g., CISOs, compliance managers).
- Implement a clear cybersecurity framework aligned with industry standards like ISO 27001 or NIST.
3. Develop a Risk Management Strategy
- Prioritise routine risk assessments covering systems, processes, and personnel.
- Use techniques like penetration testing to evaluate and address vulnerabilities.
4. Implement Protection and Detection Measures
- Adopt firewalls, intrusion detection systems, data encryption, and multi-factor authentication.
- Monitor systems for anomalies or pre-indicators of cyberattacks.
5. Train Your Workforce
Your workforce is a critical layer of cybersecurity. Invest in training sessions to ensure employees are aware of phishing and other risk vectors.
6. Test and Update Your Incident Response Plan
- Define action steps, roles, and communication channels for cyber crises.
- Regularly update and rehearse your plan through simulations and roleplay scenarios.
7. Engage With Regulators
Establish channels for ongoing dialogue with NCAs and sector-specific Computer Security Incident Response Teams (CSIRTs).
8. Frequent Reviews and Updates
Compliance is a dynamic process, so audit your measures regularly to stay ahead of new threats or regulatory updates.
Securing the Future With NIS2
The NIS2 Directive marks an important step toward a safer, more resilient digital society. While compliance may require significant effort, the benefits far outweigh the risks. Organisations that proactively adopt NIS2 not only demonstrate regulatory diligence but also gain a valuable competitive edge by safeguarding their operational and reputational integrity.
To get started on your NIS2 compliance journey, collaborate with cybersecurity experts to perform an initial assessment, implement tailored security protocols, and develop robust risk management plans.

